UML Short Introduction¶
Interface¶
Does not implement anything
C++: abstract base class
Purest form (preferred): no implementation of anything
Implementation inheritance is possible though, but should not be overused

class Sensor
{
public:
virtual ~Sensor() {}
virtual double get_temperature() = 0;
};
Interface Implementation, Inheritance¶
I2CSensoris-aSensorI2CSensorcan-be-used-as-aSensor(e.g. pointer assignment)
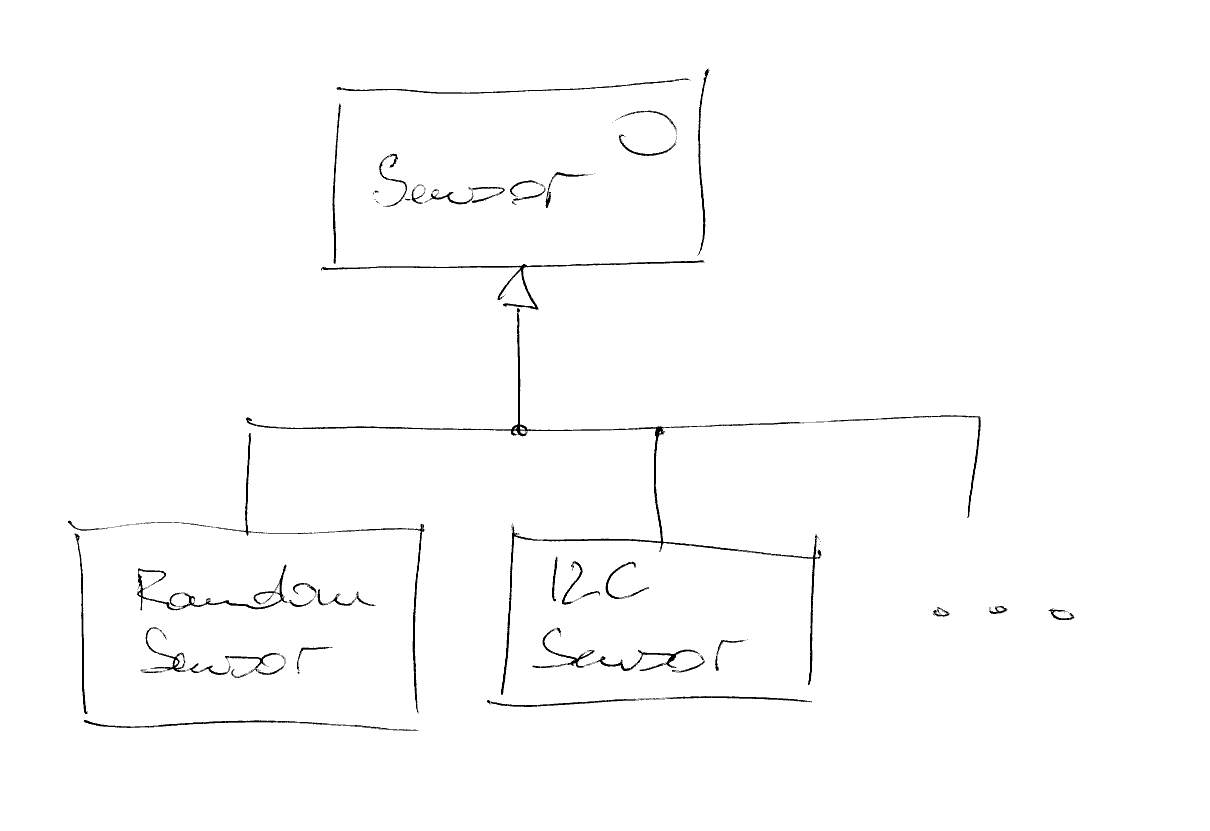
class I2CSensor : public Sensor
{
public:
I2CSensor(unsigned int bus, uint8_t address);
double get_temperature() override;
};
Connectors: Association, Aggregation, Composition¶
Several forms of knows-a
Describes using-relationships between types
Association¶
Lightest form
Usually implemented as raw pointer relationship
Lifetime and resource management unspecified
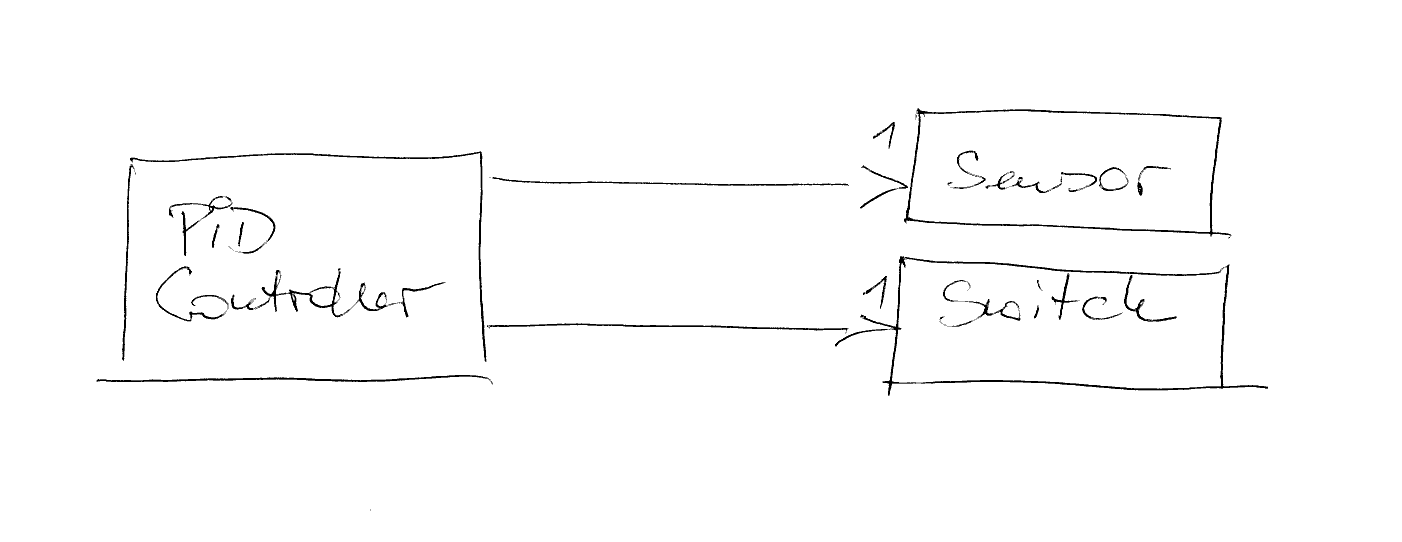
class PIDController
{
// ...
private:
Sensor* _sensor;
Switch* _switch;
};
Aggregation¶
Semi has-a
Often implemented as
std::shared_ptr<>
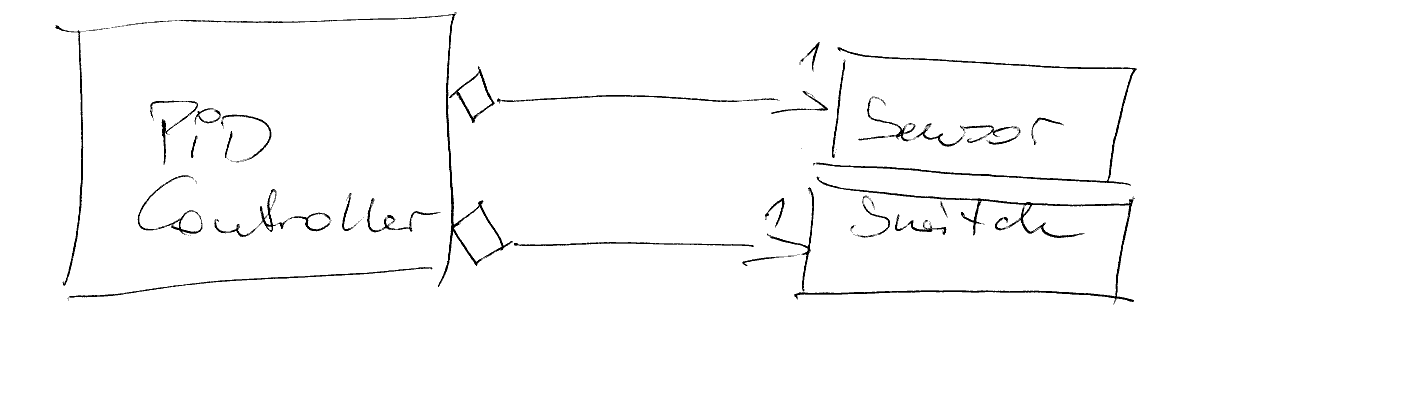
class PIDController
{
// ...
private:
std::shared_ptr<Sensor> _sensor;
std::shared_ptr<Switch> _switch;
};
Composition¶
Most-defined form
Commonly implemented as
Automatic membership
std::unique_ptr<>
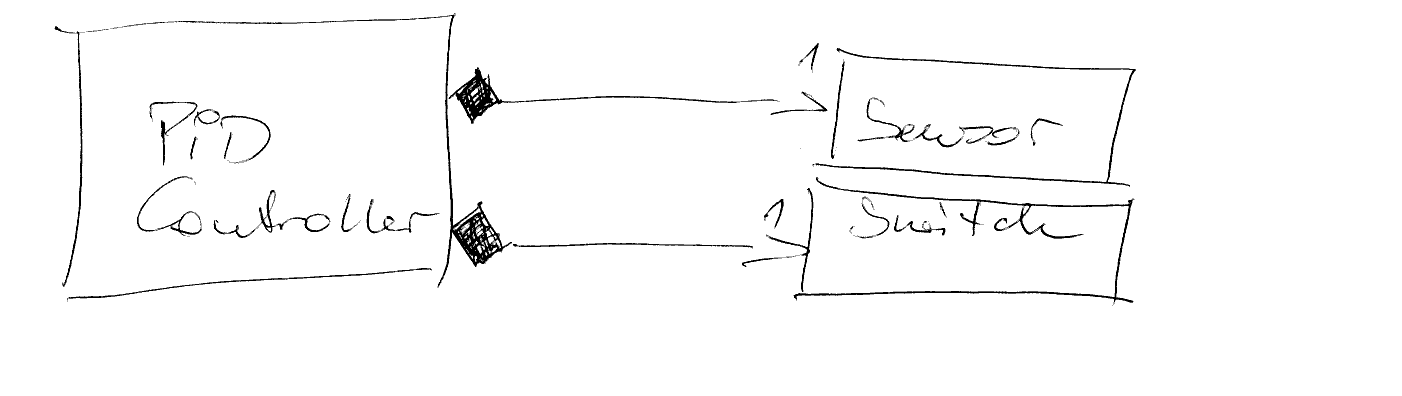
class PIDController
{
// ...
private:
Sensor _sensor;
Switch _switch;
};
class PIDController
{
// ...
private:
std::unique_ptr<Sensor> _sensor;
std::unique_ptr<Switch> _switch;
};
